duf is one of the fancy Linux disk monitoring utilities written in Golang. It is released under MIT license and It supports Linux, macOS, BSD, and even Windows too.
Features of duf
- Gives you an overview of all the devices mounted which is easy to understand
- Ability to specify a directory/file name and check free space for that mount point
- Change/Remove columns from the output
- List inode information
- Sort the output
- JSON output supported
- Ability to specify the theme if it does not detect your terminal’s theme automatically
How to install duf on Debian/Ubuntu Linux
Use the wget command or curl command to download file:
$ https://github.com/muesli/duf/releases/download/v0.6.2/checksums.txt $ wget https://github.com/muesli/duf/releases/download/v0.6.2/duf_0.6.2_linux_amd64.deb $ sha256sum --ignore-missing -c checksums.txt
Now, Install duf .deb package on Debian or Linux Mint packages:
$ sudo apt install ./duf_0.6.2_linux_amd64.deb
[ads1]
How to use Duf disk monitoring utility
Now, launch the application by simply typing duf from the terminal.
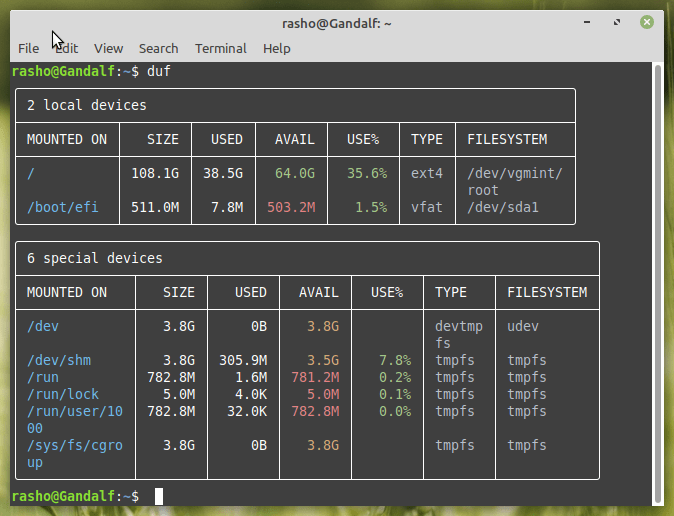
If you want to take a look at all the available commands using duf at a glance, you can type in:
$ duf --help
Usage of duf:
-all
include pseudo, duplicate, inaccessible file systems
-hide string
hide specific devices, separated with commas:
local, network, fuse, special, loops, binds
-hide-fs string
hide specific filesystems, separated with commas
-inodes
list inode information instead of block usage
-json
output all devices in JSON format
-only string
show only specific devices, separated with commas:
local, network, fuse, special, loops, binds
-only-fs string
only specific filesystems, separated with commas
-output string
output fields: mountpoint, size, used, avail, usage, inodes, inodes_used, inodes_avail, inodes_usage, type, filesystem
-sort string
sort output by: mountpoint, size, used, avail, usage, inodes, inodes_used, inodes_avail, inodes_usage, type, filesystem (default "mountpoint")
-style string
style: unicode, ascii (default "unicode")
-theme string
color themes: dark, light (default "dark")
-version
display version
-warnings
output all warnings to STDERR
-width uint
max output width
[ads1]
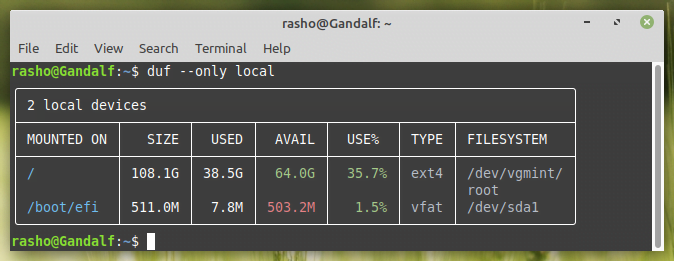
You can print only specific file systems or devices by passing it as an argument. Since I created this machine in a single partition everything is mounted on the root (/). Based upon your partition scheme you will see different output.
$ duf /home /usr /opt $ duf /root/ $ duf /var/log
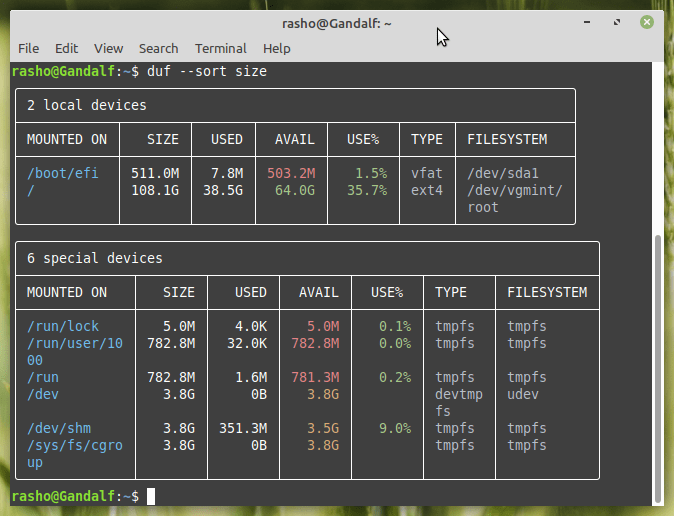
Another example would be sorting the output based on the size in a particular order, here’s what you need to type:
duf --sort size
And, the output should look like:
You can pass --all flag to display Pseudo, inaccessible, and duplicate file systems.
$ duf -all
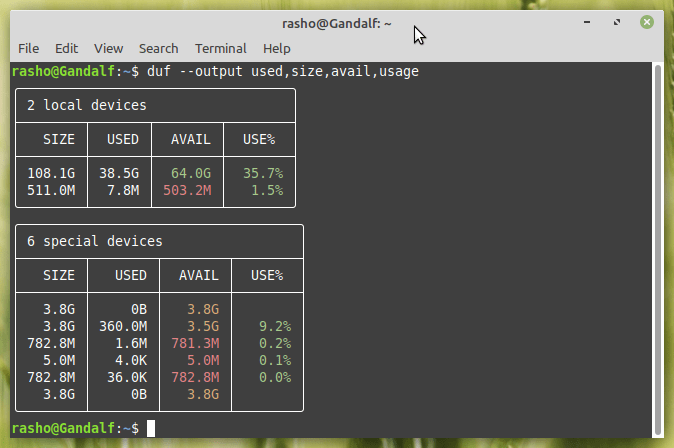
You have the option to print only certain columns bypassing the column name as an argument to --output flag. Example:
$ duf --output used,size,avail,usage
You can explore its GitHub page for more information on additional commands and installation instructions.
[ads1]
Is there anything similar to this tool that you know of? Feel free to let me know your thoughts in the comments down below.