MariaDB is a drop-in replacement for MySQL. Several Linux distributions are switching from MySQL to MariaDB as a RDBMS offering. Arch Linux and Fedora are among distributions which have already made the move. Expect adoption of MariaDB to continue, with MySQL disappearing as a default option.
With that in mind, I checked out the installation of MariaDB version 5.5.33a on CentOS. The MariaDB team have made the process very simple. It’s also nice to note the packages are signed which not only helps to ensure the integrity of the package, but is also required by some security programs.
Why MariaDB?
- MariaDB is totally open source version of MySQL
- It works just like MySQL and is compatible with MySQL setups
- Fedora and Red Hat/CentOS is moving to use MariaDB from Fedora 19/RHEL 7/CentOS 7 versions
Installing MariaDB Database in RHEL/CentOS and Fedora
We highly recommended to use custom MariaDB YUM repository to install. Create a repo file under /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo, Copy and paste following line under MariaDB repo:
Adding the MariaDB YUM Repository in RHEL/CentOS and Fedora Linux
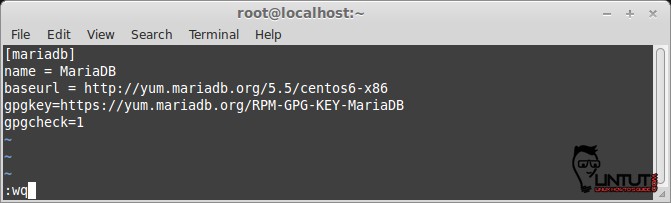
Add repository on Centos 6 32-bit
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
and paste following line:
# MariaDB 5.5 CentOS repository list # http://mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/centos6-x86 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Add repository on Centos 6 64-bit
# MariaDB 5.5 CentOS repository list # http://mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/centos6-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Add repository on RHEL 6 32-bit
# MariaDB 5.5 RedHat repository list # http://mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/rhel6-x86 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Add repository on RHEL 6 64-bit
# MariaDB 5.5 RedHat repository list # http://mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/rhel6-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Add repository on Fedora 20 32-bit
# MariaDB 5.5 Fedora repository list # http://mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/fedora20-x86 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Add repository on Fedora 18 64-bit
# MariaDB 5.5 Fedora repository list # http://mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/ [mariadb] name = MariaDB baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/5.5/fedora20-amd64 gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB gpgcheck=1
Show MariaDB repository for other distribution
Install MariaDB 5.5.33a on RHEL/CentOS 6.x and Fedora 18 linux
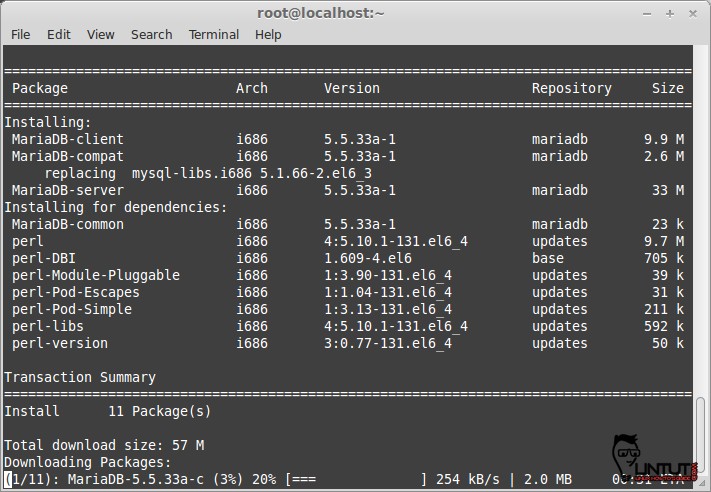
Install MariaDB using YUM command:
# yum install MariaDB-server MariaDB-client -y
Starting MariaDB
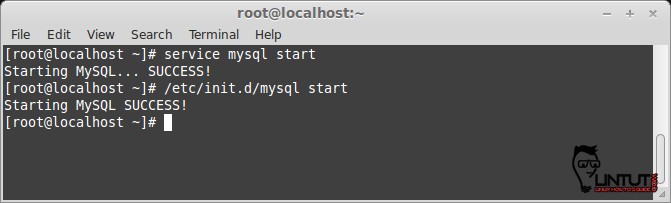
After complite installation process, start MariaDB width following command:
# service mysql start
or
# /etc/init.d/mysql start
Set MariaDB to start on boot:
# chkconfig mysql on
Secure MariaDB after installation
- Set (Change) root password
- Remove anonymous users
- Disallow root login remotely
- Remove test database and access to it
- Reload privilege tables
# mysql_secure_installation
/usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation: line 379: find_mysql_client: command not found
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Restart MariaDB:
# service mysql restart
Try to connect to MariaDB:
# mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MariaDB connection id is 1 Server version: 5.5.33a-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle, Monty Program Ab and others. Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]>
That’s it. For questions please use comments.
Reference: https://mariadb.com/kb/en/installing-mariadb-with-yum/