If you spend a lot of time at the command line you may have run into an annoying issue where your session times out after a relatively brief period of inactivity. While this is desirable from a security perspective, it can cause problems when you’re trying to perform a long running operation.
Usually what happens is that your connection to the server is reset when you’ve been idle for a while, typically producing the error: Connection reset by peer. To circumvent this, you need to set a Keep Alive option on the server.
[box type=”info” align=”” class=”” width=””]See also : Install and configure OpenSSH-server on Linux [/box]In this guide, you will learn how to prevent the SSH connection timeout and keep your SSH session alive even after some inactivity in Linux.
Increase SSH Connection Timeout
On the server, head over to the /etc/ssh/sshd_config configuration file.
$ sudo vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Scroll and locate the following parameters:
#ClientAliveInterval #ClientAliveCountMax
[ads]
Where,
ClientAliveInterval: Sets a timeout interval in seconds after which if no data has been received from the client, sshd will send a message through the encrypted channel to request a response from the client. The default is 0, indicating that these messages will not be sent to the client. This option applies to protocol version 2 only.ClientAliveCountMax: Sets the number of client alive messages which may be sent without sshd receiving any messages back from the client. If this threshold is reached while client alive messages are being sent, sshd will disconnect the client, terminating the session.
The timeout value is given by the product of the above parameters i.e.
Timeout value = ClientAliveInterval * ClientAliveCountMax
For example, let’s say you have defined your parameters as shown:
ClientAliveInterval 1200 ClientAliveCountMax 3
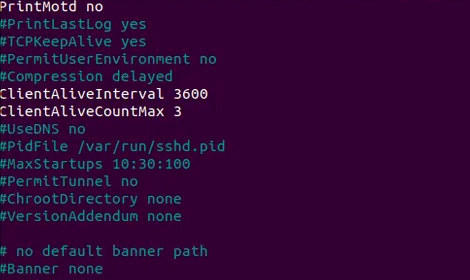
The Timeout value will be 1200 seconds * 3 = 3600 seconds. This is an equivalent of 1 hour, which implies that your ssh session will remain alive for idle time of 1 hour without dropping.
Alternatively, you can achieve the same result by specifying the ClientAliveInterval parameter alone.
ClientAliveInterval 3600
Once done, reload the OpenSSH daemon for the changes to come into effect.
$ sudo systemctl reload sshd