Bashtop is a free and open source Terminal based resource monitor for Linux, macOS and BSD systems. This tool can display usage and stats for processor, memory, disks, network and processes. Bashtop is written in Bash with a TUI interface for monitoring resource usage on your Linux, macOS or FreeBSD system.
Features of Bashtop System Resource Monitor
- Easy to use, with a game inspired menu system.
- Fast and “mostly” responsive UI with UP, DOWN keys process selection.
- Function for showing detailed stats for selected process.
- Ability to filter processes.
- Easy switching between sorting options.
- Send SIGTERM, SIGKILL, SIGINT to selected process.
- UI menu for changing all config file options.
- Auto scaling graph for network usage.
- Shows message in menu if new version is available
- Shows current read and write speeds for disks
- Multiple data collection methods which can be switched if running on Linux
[ads]
Prerequisites
- Bash 4.4 or later versions
- Git
- GNU Coreutils
- GNU sed, awk, grep and ps command-line tools.
- Lm-sensors – optional – (For gathering CPU temperature statistics).
1. Install Bashtop Resource Monitor on Ubuntu and Linux Mint
You can use PPA repository for Ubuntu Linux installations:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:bashtop-monitor/bashtop $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install bashtop
2. Install Bashtop Resource Monitor on Debian
Bashtop is available in Debian’s official repository. To install it, simply run the command:
$ sudo apt install bashtop
Also, you can run the commands shown.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install git $ git clone https://github.com/aristocratos/bashtop.git $ cd bashtop/ $ cd DEB $ sudo ./build
For uninstallation, use the command:
$ sudo ./build --remove
3. Install Bashtop in Fedora, CentOS 8 and RHEL 8
To get Bashtop into Fedora, simply run the command:
$ sudo dnf install bashtop
On CentOS 8, enable EPEL and PowerTools repositories:
$ sudo dnf install -y epel-release $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled PowerTools $ sudo dnf install bashtop
[ads]
If running RHEL 8 Linux, you need codeready repository:
$ ARCH=$( /bin/arch )
$ sudo subscription-manager repos --enable "codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-${ARCH}-rpms"
$ sudo dnf install epel-release
$ sudo dnf install bashtop
4. Install Bashtop on Arch Linux
Bashtop is available in AUR as bashtop-git. To install Bashtop, simply run:
$ sudo pacman -S bashtop
How to Use Bashtop Resource Monitor on Linux
Now that we installed the bashtop, it is time to start it and see the application in all TUI (Text-based user interface ) glory:
$ bashtop
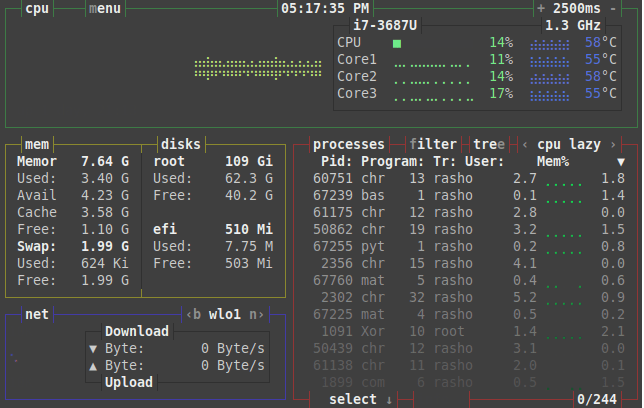
We can use the following keys to control the Linux/Unix process and other operations of the bashtop application as per our needs.
| Shortcode | description |
|---|---|
| Esc, M, m | Shows main menu. |
| F2, O, o | Shows options. |
| F1, H, h | Shows this window. |
| Ctrl-C, Q, q | Quits program. |
| +, A, a -, S, s | Add/Subtract 100ms to/from update timer. |
| Up Down | Select in process list. |
| Enter | Show detailed information for selected process. |
| Pg Up Pg Down | Jump 1 page in process list. |
| Home End | Jump to first or last page in process list. |
| Left Right | Select previous/next sorting column. |
| b, B n, N | Select previous/next network device. |
| E, e | Toggle processes tree view |
| R, r | Reverse sorting order in processes box. |
| F, f | Input a string to filter processes with. |
| C, c | Clear any entered filter. |
| Selected T, t | Terminate selected process with SIGTERM – 15. |
| Selected K, k | Kill selected process with SIGKILL – 9. |
| Selected I, i | Interrupt selected process with SIGINT – 2. |
Conclusion
Bashtop provides an excellent way of keeping an eye on your Linux system resources. However, it’s much slower than top and htop and is a bit resource-intensive. You can find more information and documentation about the project on its Github page here: https://github.com/aristocratos/bashtop
I loved it. Nice tool but slow on my old server. Htop is much better than anything else.