Duc is a collection of tools for indexing, inspecting and visualizing disk usage. Duc maintains a database of accumulated sizes of directories of the file system, and allows you to query this database with some tools, or create fancy graphs showing you where your bytes are.
Duc comes with a command line tool called duc, which is used to create, maintain and query the disk usage database.
Duc features:
-
- Built to scale to huge filesystems.
- Fast in operation – disk usage is stored in an optimized database.
- Various sub-commands for querying or exploring the index:
- duc info shows a list of available directory trees in the database, and the time and date of the last scan.
- duc ls lists all files and directories under the given path on the console.
- duc ui runs a ncurses based console user interface for exploring the file system usage.
- duc gui starts a graphical (X11) interface representing the file system in a sunburst graph.
- Handles multiple path arguments.
- DPI handing for graph font size.
[ads1]
Install Duc in Linux
Duc is available in the default repositories of Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu. So installing Duc on DEB-based systems is a piece of cake.
$ sudo apt-get install duc
On other Linux distributions, you may need to manually compile and install Duc from source as shown below.
Download latest duc source .tgz file from the releases page on github. As of writing this guide, the latest version was 1.4.4.
$ wget https://github.com/zevv/duc/releases/download/1.4.4/duc-1.4.4.tar.gz
Then run the following commands one by one to install DUC.
$ tar -xzf duc-1.4.4.tar.gz $ cd duc-1.4.4 $ ./configure $ make $ sudo make install
Using Duc
The typical usage of duc is:
$ duc
You can view the list of general options and sub-commands by running the following command:
$ duc help
Let us now ses some practical use cases of duc utility.
1. Create Duc database
First of all, you need to create an index file (database) of your filesystem. To create an index file, use “duc index” command.
For example, to create an index of your /home directory, simply run:
$ duc index /home
The above command will create the index of your /home/ directory and save it in $HOME/.duc.db file.
[ads]
2. Query Index
Duc has various sub-commands to query and explore the index.
To view the list of available indexes, run:
~$ duc info Date Time Files Dirs Size Path 2021-04-14 11:47:37 108.4K 13.1K 23.8G /home
To list all files and directories in the current working directory, you can do:
$ duc ls
3. Visualize Disk Usage
To show the graph of a given path, use “ls” subcommand like below.
$ duc ls -Fg /home/Documents
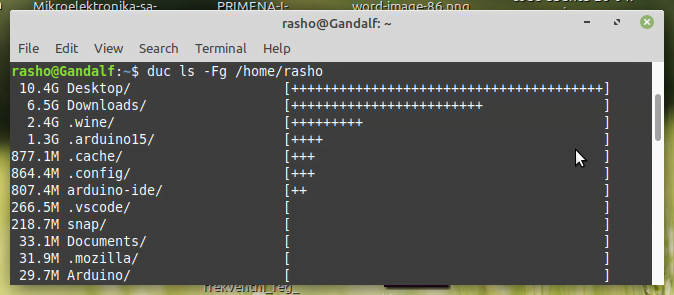
duc ls commandAs you see in the above output, the ls subcommand queries the duc database and lists the inclusive size of all
files and directories of the given path i.e /home/rasho/ in this case.
Here, the -F option is used to append file type indicator (one of */) to entries and the -g option is used to draw graph with relative size for each entry.
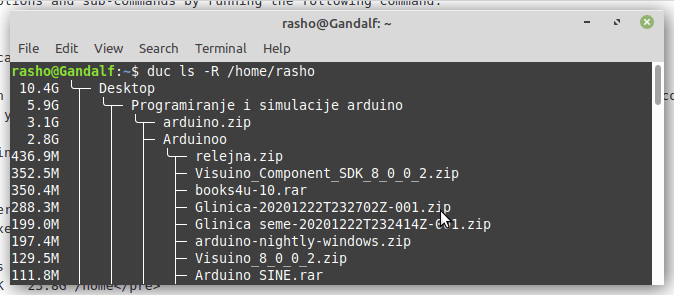
You can use -R option to view the disk usage result in tree structure.
$ duc ls -R /home/rasho
[ads1]
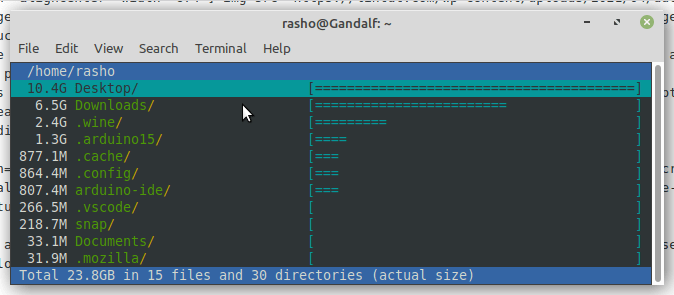
To query the duc database and open a ncurses based console user interface for exploring the disk usage of given path, use ui subcommand like below.
$ duc ui /home/rasho
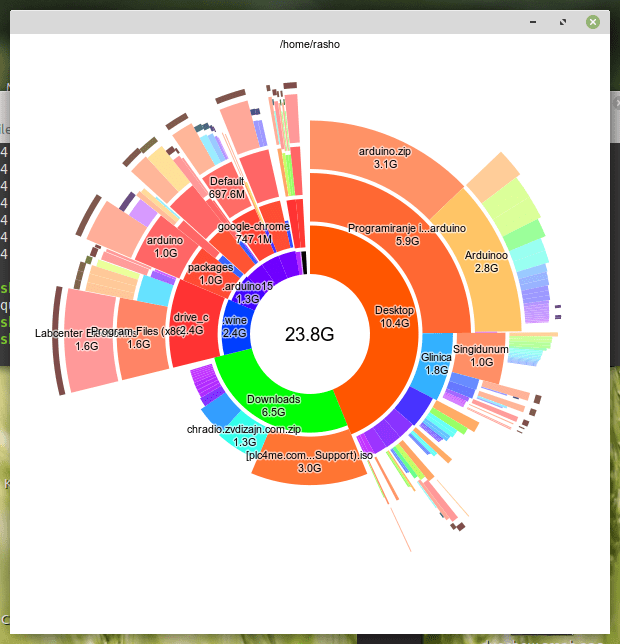
4. Use a graphical interface (X11)
If you prefer use a graphical interface (X11) to explore the file system, the command that can be used is the following:
$ duc gui
Example output:
That is all. Is there anything similar to this tool that you know of? Feel free to let me know your thoughts in the comments down below.
See also:
[box type=”info” align=”” class=”” width=””]
[/box]