The linux ip command is similar to ifconfig, but more powerful and is intended to be a replacement for it. With ip you have the advantage of performing several network administration tasks with only one command.
In this tutorial, we are going to discuss 15 most common uses for ‘ip’ command, so let’s get going.
1. Identify available network interface with ip command
If you run ip link show command it will list all available network interfaces on your server.
$ ip link show
Example output:
$ ip link show
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:64:ab:7a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
2. How to Check an IP Address
To get the depth information of your network interfaces like IP Address, MAC Address information, use the following command as shown below.
$ ip addr show
The output will display the currently assign IP configuration for all network interfaces.
$ ip addr show
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:64:ab:7a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.100.8/24 brd 192.168.100.255 scope global enp0s3
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.100.20/24 scope global secondary enp0s3:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe64:ab7a/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3. How to Enable Network Interface
The “up” flag with interface name (enp0s3) enables a network interface. For example, the following command will activates the enp0s3 network interface.
$ ip link enp0s3 up Or $ sudo ip link set enp0s3 up
4. How to Disable Network Interface
The “down” flag with interface name disables a network interface. For example, the following command will De-activates the enp0s3 network interface.
$ ip link set enp0s3 down or $ sudo ip link set enp0s3 down
[ads]
5.How to Assign a IP Address to Specific Interface
To assign IP address to interface, we will use:
$ sudo ip addr add 192.168.100.4/255.255.255.0 dev enp0s3
We can also set broadcast address to interface with ‘ip’ command. By default no broadcast address is set, so to set a broadcast address command is:
$ $ sudo ip addr add broadcast 192.168.100.255 dev enp0s3
We can also set standard broadcast address along with IP address by using the following command,
$ sudo ip addr add 192.168.100.4/24 brd + dev enp0s3
As shown in the above example, we can also use ‘brd’ in place on ‘broadcast’ to set broadcast ip address.
6. How to Remove an IP Address
The following command will remove an assigned IP address from the given interface:
$ sudo ip addr del 192.168.100.4/24 dev enp0s3
7. Adding an Alias for an interface
To add an alias i.e. assign more than one IP to an interface, execute below command:
$ sudo ip addr add 192.168.100.20/24 dev enp0s3 label enp0s3:1
Example outputs:
$ ip addr show enp0s3
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:64:ab:7a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.100.8/24 brd 192.168.100.255 scope global enp0s3
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.100.20/24 scope global secondary enp0s3:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe64:ab7a/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
8. Check routing table
Checking routing information shows us the route a packet will take to reach the destination. To check the network routing information, execute the following command:
$ ip route show
Example output:
$ ip route show default via 192.168.100.1 dev enp0s3 proto static 192.168.100.0/24 dev enp0s3 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.100.8
Suppose now that you have an IP address which you need to know the route packets will take. You can use route option as follows:
$ ip route get 192.168.100.4
9. Adding a static route
To change the default route, the ip command can be used as follows:
$ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.100.150/24
So now all network packets will travel via 192.168.100.150 as opposed to old default route. For changing the default route for a single interface & to make change route further, execute
$ sudo ip route add 10.0.0.2 via 192.168.100.150/24 dev enp0s3
10. Removing a static route
To remove assigned static route, simply type the following command.
$ sudo ip route del 10.0.0.2
11. How do i add default gateway
Default gateway can be specified globally or for in interface-specific config file. Advantage of default gateway is If we have more than one NIC is present in the system. You can add default gateway on the fly as shown below command.
sudo ip route add default via 192.168.100.1
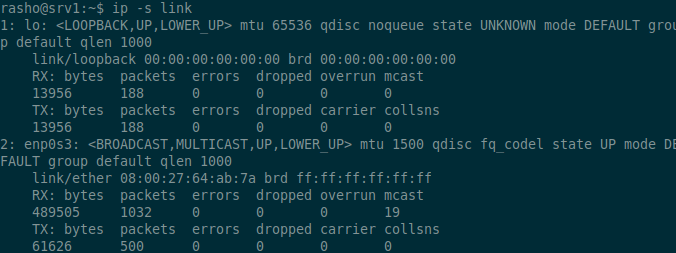
12. Show network statistics
The ip command can also be used to show the statistics of the various network interfaces. To do this you can use the ip command with the option -s and then specify the network device.
$ ip -s link
[ads]
When you need to get information about a particular network interface, add the option ls followed by the name of the network interface. The option -s when used more than once gives you more information about that particular interface. This can be very useful especially when trouble shooting errors in network connectivity.
ip -s -s link ls enp0s3
13.Checking ARP entries
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to translate an IP address to its corresponding physical address, commonly known as MAC address. With ip command you can view the MAC address of the devices connected in your LAN by using the option neigh or neighbour.
$ ip neigh
14. Monitor netlink messages
It is also possible to view netlink messages with ip command. The monitor option allows you to see the state of your network devices. For instance a computer on your LAN could be categorized as REACHABLE or STALE depending on its status. The command can be used as follows:
$ ip monitor all
Example output:
$ ip monitor all [NEIGH]192.168.100.4 dev enp0s3 lladdr c8:f7:33:de:30:d7 REACHABLE [NEIGH]192.168.100.4 dev enp0s3 lladdr c8:f7:33:de:30:d7 STALE [NEIGH]192.168.100.4 dev enp0s3 lladdr c8:f7:33:de:30:d7 PROBE [NEIGH]192.168.100.4 dev enp0s3 lladdr c8:f7:33:de:30:d7 REACHABLE
15. View help
If you want to find a option which is not listed in above examples, then you can look for manual.
$ man ip
Conclusion
The command ip is a must have tool for network administrators and all Linux users alike. It is time to move from ifconfig, especially when you are writing scripts.