ifconfig command is used to configure a network interfaces in GNU/Linux systems. It displays the details of a network interface card like IP address, MAC Address, and the status of a network interface card etc. But, this command is obsolete, and is not found in the minimal versions of RHEL 7 and its clones like CentOS 7, Oracle Linux 7, and Scientific Linux 7.
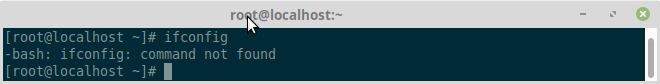
In this tutorial we will show you how to install ifconfig on centos 7. By default ifconfig command will be not found in fresh installation centos 7 so we need to install package first to use ifconfig command.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of linux, know how to use the shell, root user or non-root user account with sudo privileges set up on your server.
How do I enable and use “ifconfig” Command in CentOS 7 minimal servers?
If you don’t know where to find the ifconfig command, follow the simple steps provided below. First let us find out which packages will provide ifconfig command. To do that, enter the following command:
# yum provides */ifconfig
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: centos.t-2.net
* extras: centos.t-2.net
* updates: centos.t-2.net
net-tools-2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7.x86_64 : Basic networking tools
Repo : base
Matched from:
Filename : /sbin/ifconfig
[ads]
As you see in the above output, the net-tools package provides the ifconfig command. So, let us install net-tools package to use ifconfig command.
# sudo yum instll net-tools -y
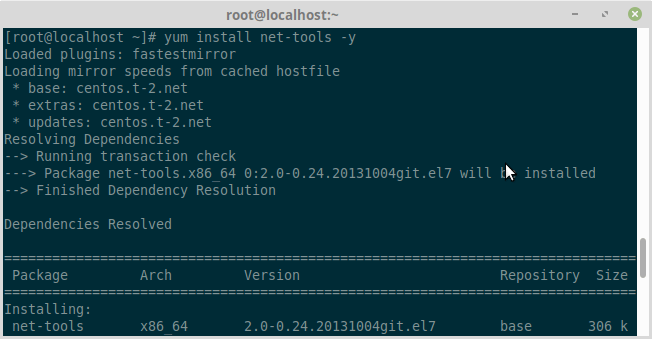
Now, you’ll be able to use the command ifconfig as usual.
[root@localhost ~]# ifconfig
enp0s3: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.100.5 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.100.255
inet6 fe80::72fa:5672:4f5d:ea72 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 08:27:72:da:42:65 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 13534 bytes 18672794 (17.8 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2882 bytes 221122 (215.9 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 132 bytes 11664 (11.3 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 132 bytes 11664 (11.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
That’s All. You now have the ifconfig command available on your CentOS 7 machine.
See also:
How to configure static ip address on CentOS 7
How to setup network after RHEL/CentOS 7 minimal installation
Thank you, I also learned the skill of “yum provides” 🙂