MyCLI is a command line interface for MySQL, MariaDB, and Percona with auto-completion and syntax highlighting. The auto-completion will help you write queries faster and with ease. The REPL (Read, Eval, Print, Loop) will pop up a suggestion menu as soon as you start typing. The suggestions are context sensitive based on the position of the cursor. eg: Only tables are suggested after the FROM keyword, only column names are suggested after the WHERE clause.
MyCLI Features
- Auto-completion as you type for SQL keywords as well as tables, views, and columns in the database.
- Syntax highlighting of input while typing.
- Support for multiline queries.
- Allows you to save your favorite queries.
- Prints tabular data in an appealing way.
- Support for SSL connections.
- Smart-completion (enabled by default) will suggest context-sensitive completion.
- Log every query and its results to a file.
How to Install MyCLI for MySQL and MariaDB in Linux
On Debian/Ubuntu distributions, you can easily install the MyCLI package using the apt command.
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install mycli
Fedora has a package available for MyCLI. Install it using dnf command as shown below.
$ sudo dnf install mycli
For other Linux distributions such as RHEL/CentOS, you’ll need Python pip tool to install mycli. Start by installing pip with the commands below:
$ sudo yum install pip
Once pip is installed, you can install mycli as follows:
$ sudo pip install mycli
[ads]
How to Use MyCLI for MySQL and MariaDB in Linux
Here is a small demo:
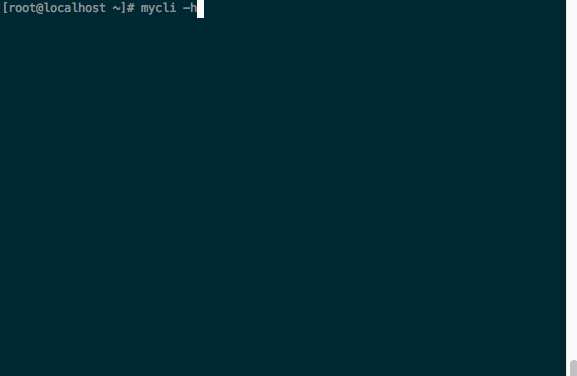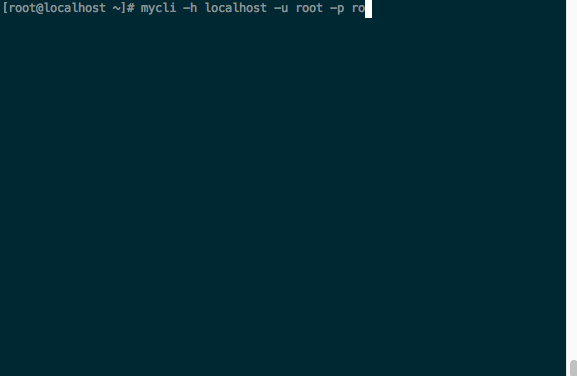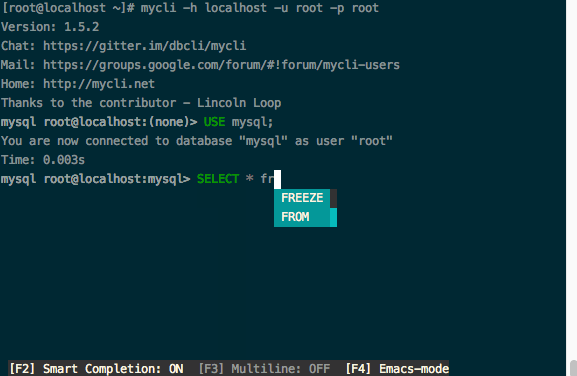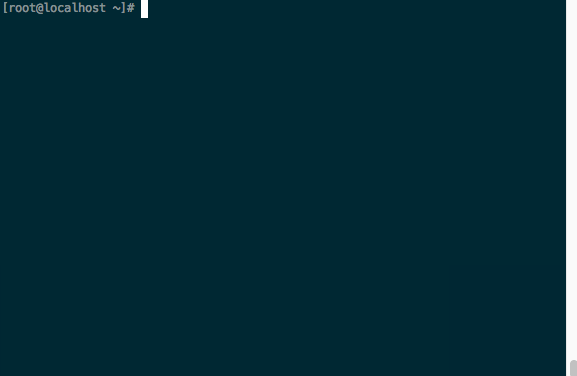
To view usage man page, use the command:
# mycli --help
Usage: mycli [OPTIONS] [DATABASE]
Options:
-h, --host TEXT Host address of the database.
-P, --port INTEGER Port number to use for connection. Honors
$MYSQL_TCP_PORT
-u, --user TEXT User name to connect to the database.
-S, --socket TEXT The socket file to use for connection.
-p, --password TEXT Password to connect to the database
--pass TEXT Password to connect to the database
--ssl-ca PATH CA file in PEM format
--ssl-capath TEXT CA directory
--ssl-cert PATH X509 cert in PEM format
--ssl-key PATH X509 key in PEM format
--ssl-cipher TEXT SSL cipher to use
--ssl-verify-server-cert Verify server's "Common Name" in its cert
against hostname used when connecting. This
option is disabled by default
-v, --version Version of mycli.
-D, --database TEXT Database to use.
-R, --prompt TEXT Prompt format (Default: "\t \u@\h:\d> ")
-l, --logfile FILENAME Log every query and its results to a file.
--defaults-group-suffix TEXT Read config group with the specified suffix.
--defaults-file PATH Only read default options from the given file
--auto-vertical-output Automatically switch to vertical output mode
if the result is wider than the terminal
width.
-t, --table Display batch output in table format.
--warn / --no-warn Warn before running a destructive query.
--local-infile BOOLEAN Enable/disable LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE.
--login-path TEXT Read this path from the login file.
-e, --execute TEXT Execute query to the database.
--help Show this message and exit.
That’s all! In this guide, we showed how to install and use mycli with simple commands in Linux. Do share your thought concerning this article via the feedback form below.
Awesome, works perfectly fine much like what the fish shell does to the Linux terminal.