Secure shell (SSH) is a network protocol providing shell services on a remote machine via a secure channel. OpenSSH is an open-source implementation of the ssh protocol, allowing encrypted communication over a network via a suite of software.
OpenSSH is developed by the Open BSD group and it is released under Simplified BSD License.
OpenSSH features
The following is a list of OpenSSH features:
- Open Source Project
- Free Licensing
- Strong Encryption (3DES, Blowfish, AES, Arcfour)
- X11 Forwarding (encrypt X Window System traffic)
- Port Forwarding (encrypted channels for legacy protocols)
- Strong Authentication (Public Key, One-Time Password and Kerberos Authentication)
- Agent Forwarding (Single-Sign-On)
- Interoperability (Compliance with SSH 1.3, 1.5, and 2.0 protocol Standards)
- SFTP client and server support in both SSH1 and SSH2 protocols.
- Kerberos and AFS Ticket Passing
- Data Compression
More about OpenSSH features read here.
OpenSSH installation
Install OpenSSH on RHEL/CentOS 5.x/6.x
To install OpenSSH and auto-start OpenSSH server on CentOS or RHEL type following command:
# yum -y install openssh-server openssh-clients # service sshd start # hkconfig sshd on
Install OpenSSH on Fedora 15/16/17/18/19
To install OpenSSH and auto-start OpenSSH server on Fedora 15/16/17/18/19 type following command:
# sudo yum -y install openssh-server openssh-clients # sudo service sshd start # sudo systemctl enable sshd.service
Install OpenSSH on Debian/Ubuntu based distribution
To install OpenSSH and auto-start OpenSSH server on Debian/Ubuntu based distribution, type following command:
# sudo apt-get install openssh-server openssh-client # sudo update-rc.d ssh defaults
How to login to OpenSSH
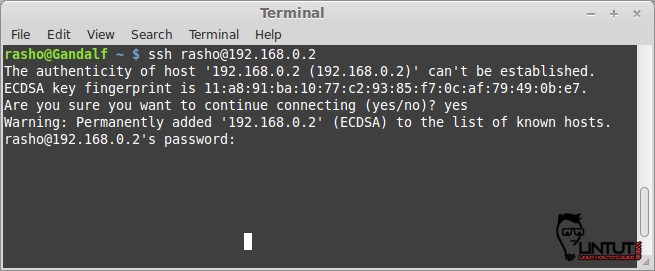
To login to your computer from a Unix-like machine, go to a command-line and type:
# ssh username@ipaddress # ssh username@hostname
For example:
# ssh rasho@192.168.0.2
Configure OpenSSH server
If you would like to configure OpenSSH server edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config OpenSSH configuration file.
There are a couple of OpenSSH options you may be interested in:
Port 22
By default, sshd listens on port 22 to listen for incoming ssh connections. By changing the default ssh port, you may be able to avert various automated attacks from hackers.
PermitRootLogin no
The PermitRootLogin option tells whether root can log in to the system via ssh.
AllowUsers user1 user2
Using the AllowUsers option, you can selectively disable ssh service for particular Linux users. You can specify multiple users separated by space.
Once you have modified /etc/ssh/sshd_config, make sure to restart ssh service.
To restart OpenSSH on Ubuntu or Debian:
# sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
To restart OpenSSH on CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:
# service sshd restart
Read also: Disable or Enable SSH Root Login and Limit SSH Access in Linux